How to Optimize (SEO Checklist) Website for Worldwide Visibility

Your website is one of your most powerful tools to attract customers, but what happens when a website is not properly optimised? If your website is not fast, easy to use, and built for search engines, you are surely going to miss out on traffic, leads, and sales. A properly optimised website does more than just look good. It actually delivers results. It can bring in leads, get people to explore your pages, and help them turn into customers that pay.
After all that effort building your site, it can be frustrating when no one is clicking. Or if they do, they leave quickly. That generally happens when the site is not giving a good user experience or is not search-friendly.
Once your site is structured for clarity, speed, and relevance, it starts attracting organic traffic and delivering a smooth experience across devices.

This is your on-page SEO guide that covers everything you need to make your website optimised for globally recognised search engines. We are going to walk you through everything you need to check, fix, and improve so your website performs better, ranks higher, and converts more leads.
Set Up SEO Foundation(GA4/GSC) the Right Way
Before you jump directly into SEO content optimization changes or link building, make sure your website has a strong SEO foundation. This setup stage helps search engines understand, crawl, and index your website successfully. It also makes sure you are tracking performance correctly.
Here is how you can do this stage by stage:
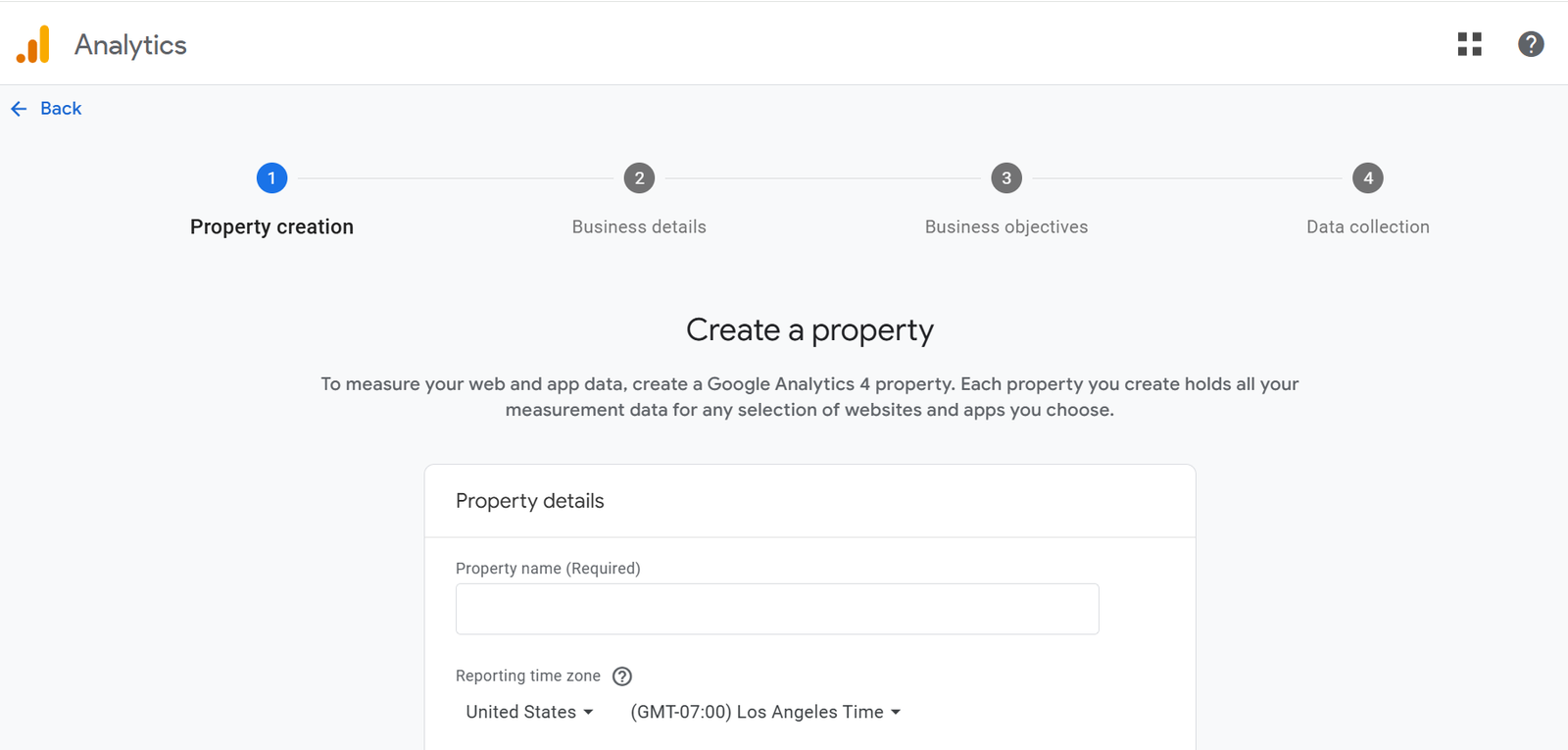
Installing Google Analytics and checking for duplicates
It shows you where your visitors come from and what kind of activity they did. But most of the time, websites have multiple versions of the tracking code. It can fill up data and make analysis misleading.
What to do:
- Use Google Tag Assistant or Chrome DevTools to check if multiple GA scripts are running.
- Make sure only one version of the GA4 tag is installed.
- Skip the GA code if you are using Tag Manager.
Note: These things matter because mess free and accurate data help you make decisions. Without it, you are just guessing.
Google Search Console
It acts as your direct line to Google. It gives a view of how your site shows up online. It allows you to track keyword performance and fix crawling or indexing issues.
Set it up at Google Search Console
Once your property is added, you will now be able to:
- Submit sitemaps
- Monitor keyword rankings
- Check indexing status
- See mobile usability and performance reports
Verifying site ownership and connecting important tools
Once Search Console is set up, you will need to verify site ownership. Google gives you several ways to do this:
- HTML tag in your section
- DNS record update
- Google Analytics or Google Tag Manager verification
While you’re at it, connect your site to other useful tools:
- Google Analytics (GA4)
- Bing Webmaster Tools
All these tools together give you a complete view of your site’s visibility and performance.
Checking for crawl errors and manual actions
In Search Console, go to the “Pages” and “Security & Manual Actions” sections and look for:
- 404 pages (pages that no longer exist)
- Server errors (5xx)
- Blocked URLs
- Unnatural links or spam issues
Fix any crawl errors using 301 redirects or by updating internal links. If you have received a manual action, then review the issue. After that, submit a reconsideration request after resolving it.
Important Note: According to a report by Ahrefs, 66.5% of pages have zero backlinks and may be hard for Google to crawl if not internally linked well.
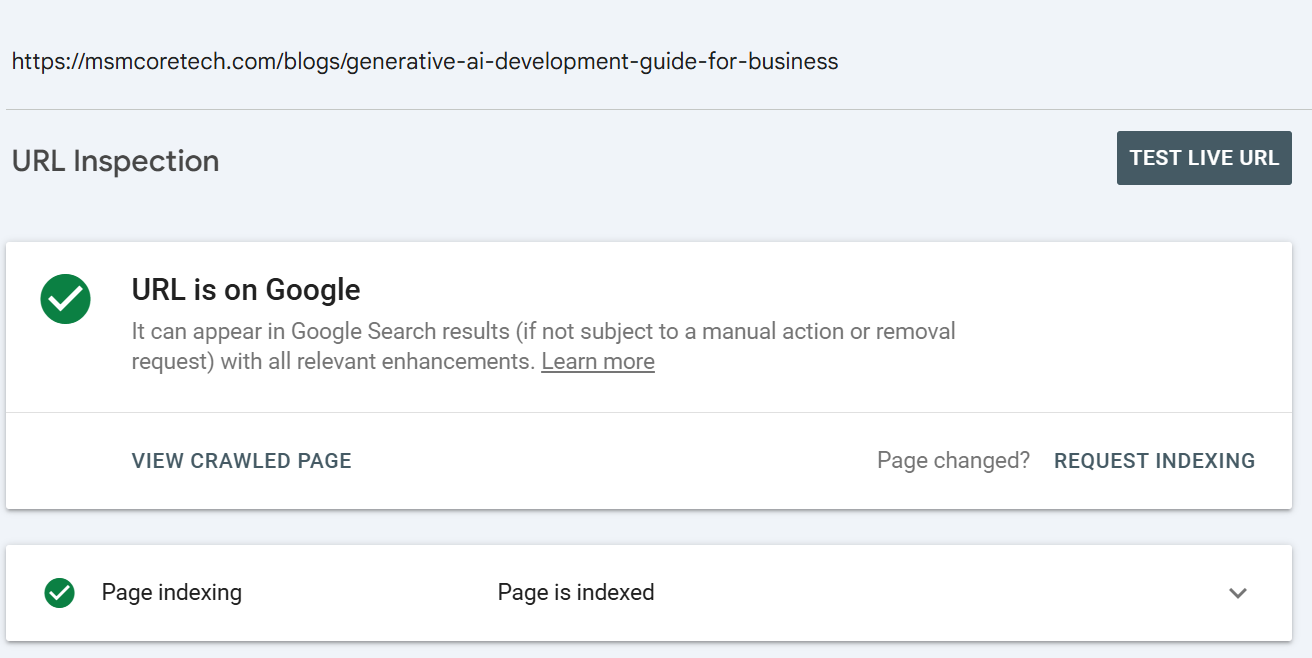
Make sure your site is indexed correctly using GSC
Even though your pages are live, that doesn’t mean they are indexed. To check if they are:
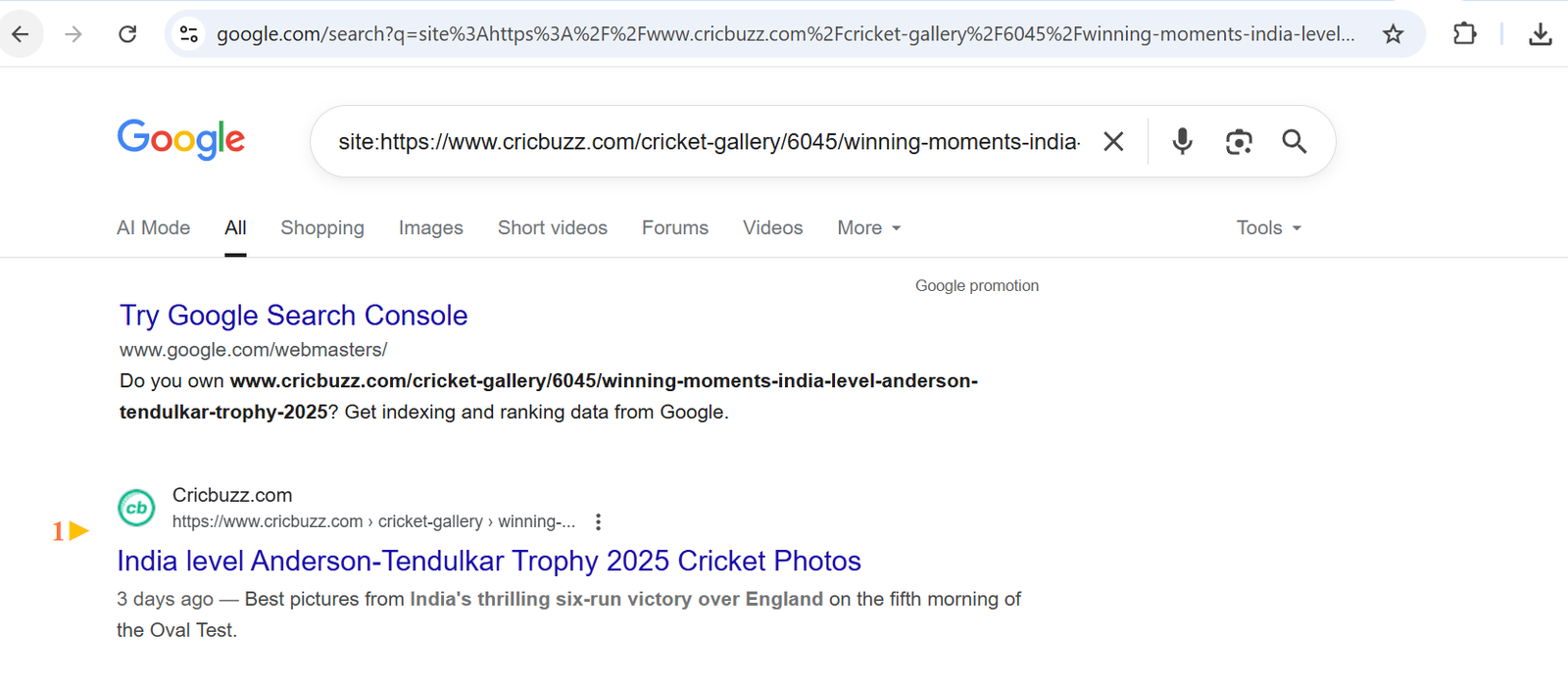
- Type ‘site:yourdomainname’ with a ‘.com’ in Google to see which pages are indexed.
- Use the “URL Inspection” tool (in Google Search Console) to see if key pages are indexed and when they were last crawled.
Creating and submitting an optimized sitemap
It tells Google what pages are there on your website. It lists all the important resource locator links on your site that should be crawled and indexed.
To create a sitemap:
- Use a tool like Yoast SEO on WordPress, or you can create one with Screaming Frog.
- Make sure it only has clean and indexable URLs and is free of redirects, errors, or duplicates.
After that, submit it in Search Console under Index, then Sitemaps.
Handling sitemap errors, invalid pages, and index differences
Since you have submitted it, do check if there are any errors, warnings, or differences.
If you notice any kind of error, they can be:
- Pages are blocked in robots.txt
- Pages are set to noindex
- There are crawl budget issues
To remove it, clean up the sitemap and fix the URLs. Then resubmit and monitor indexing over the next few days.
Run a Technical SEO Health Check
Fix any technical issues that are slowing your site down. It makes sure your site is safe, fast, and also crawlable. This will help rank better and give users a smoother experience.
Check SSL Certificate and HTTPS Redirection
Make sure your site has a valid Secure Sockets Layer and sends all HTTP traffic to HTTPS. Avoid mixed content errors. According to a transparency report from Google, it has shown that over 95% of websites on Chrome now use HTTPS.
Fix Broken Links
Your site can be affected by broken links. It can frustrate users. Tools like Screaming Frog or Ahrefs help find and fix these broken links.
Fix internal broken links by:
- Updating to the correct URL
- Removing outdated links
- Redirecting if the target page has moved
Handle Redirect Chains and Loops
Chains (A > B > C) and loops (C > B > C) make pages load slower and mess with crawlers. They also waste link equity.
To fix:
- Limit redirects to one step whenever possible
- Use 301 redirects for permanent moves
- Regularly audit your redirects using Screaming Frog or Sitebulb
Make Sure Robots.txt is Working Correctly
Your robots.txt controls what search engines can and can’t access. Double-check it's not blocking important pages and test it using Google Search Console.
Meta Robots Tag Configuration
Meta robots tags control indexing on a page by page basis.
Check if your important pages have:
- index, follow (what most pages should use)
- No accidental noindex on pages like any blog posts or any product pages.
Meta robots tag configuration is important for controlling how search engines crawl and index your pages. This impacts your visibility in search results.
Example of meta robots tags for an e-commerce website:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /cart/
Disallow: /checkout/
Disallow: /my-account/
Disallow: /search/
Disallow: /wishlist/
Allow: /product/
Allow: /category/
Allow: /images/
Sitemap: https://www.example.com/sitemap.xml
Example of meta robots tags for a general website:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /admin/
Disallow: /login/
Disallow: /signup/
Disallow: /user/
Allow: /
Sitemap: https://www.example.com/sitemap.xml
Minify CSS, JS, and HTML
It is a process that removes extra characters like spaces and line breaks from your code to reduce file size and speed up loading. You can use tools like
- Minifier
- Autoptimize
- Built-in options in platforms like Webflow or Shopify
Make sure to test after minifying, as it breaks functionality.
Use of Canonical URLs
If your site has duplicate content (the same product page accessible via multiple URLs), canonical tags tell search engines which version is the “master.”
Use canonical tags to:
- Consolidate link equity
- Avoid duplicate content penalties
- Improve crawl efficiency
Set HSTS Policy and Subdomain Redirects
HTTP Strict Transport Security forces browsers to only use HTTPS when visiting your site. It adds a layer of protection against downgrade attacks.
To enable HSTS:
- Configure it via your server or hosting panel
- Add your domain to the HSTS preload list
- Redirect all subdomains to a consistent HTTPS version
Remove Malware, Fix Security Issues
Google demotes hacked or infected sites so always scan for malware and vulnerabilities.
Tools you can use:
- Sucuri SiteCheck
- Google Search Console > Security Issues
- Hosting provider’s malware scanner
Make sure your CMS, tools, and themes are updated on a regular basis. Security should never be a side note.
Remove Chrome Console and Validation Errors
Open your website link in the Chrome browser and hit F12. After that, check the Console tab to find any warnings or errors. There are some common issues that you can find are
- Mixed content (loading HTTP on HTTPS)
- JavaScript not loading
- Deprecated functions
- CORS or policy errors
Use tools like W3C Validator to check HTML markup errors. Clean code is not just for developers. It also makes your site faster, easier to crawl, and more trustworthy.
Implement Schema Markup
Use schema markup to optimize your search results.
Schema makes your site eligible for rich snippets in search results. Boost your visibility and improve click-through rates.
Helps search engines understand your content better by connecting entities and topics.
What Schema Markup Is Used For?
Schema gives search engines the best chance of interpreting your content correctly.
It helps users discover your site more easily.
Some common types of Schema
Businesses and Organizations
Show things like name, logo, contact details, and social links. Helps with brand positioning in search.
Events
Include information like date, time, and location. Makes your listing more noticeable in search results.
Profile Pages
Ideal for personal or company profiles. Can show information like job titles, social handles, and accomplishments.
Products
Display pricing, availability, and reviews in search results.
Recipes
Include ingredients, cooking times, and ratings. Makes your content stand out in food searches.
Reviews
Add star ratings and reviewer details. This increases trust and click rates.
Videos
Improve how your videos show up in search. Include details like duration, upload date, and thumbnail.
Job Postings
Show salary, location, and job type. Helps your listing surface in job searches.
Datasets
Highlight structured data for research and statistics.
Articles
Make your news or blog posts eligible for rich features like carousels.
Discussion Forums
Show questions and answers clearly in results.
Carousel
Combining multiple items like articles, products, or recipes into a search result.
Local Business
Shows opening hours, address, and contact information. Helps you stand out in local searches.
Clean Up Your Site Architecture
A website structure should be clean and logical. On the other hand, poor architecture buries important content and confuses crawlers.
Choose the Right URL Structure
Always keep the URL short, simple, and readable. Using lowercase letters, hyphens but not underscores, and clear keywords is important. Use this as an example:
| URL Idea | Remark |
|---|---|
| /services/web-development | Clear and simple |
| /page?id=37&ref=web_dev | Not clear, no targeted word |
Avoid using bold or messy URLs unless needed.
Plan Your Site Structure and Silos
Group related content into logical silos or categories.
For instance:
- Group all SEO-related blogs under /blog/seo/.
This makes it easy for users to browse and even easier for search engines to understand the themes of your content.
Use of Breadcrumbs, Category Pages, and Internal Linking
Breadcrumbs show users where they are. Category pages help organise content, while internal links keep users exploring and pass SEO value across pages. Every important page should be just a few clicks away from others.
Reduce Click Depth (No Important Content Beyond 4 Clicks)
It is a problem if a user or even a Googlebot has to click five or six times to reach your service or product listing page.
The important content of the page can not be more than three or four clicks away from your homepage. Simplify your site structure so pages are easier to find.
Optimize Primary and Footer Navigation
Your top menu should show your main pages and services. The footer is to include include links to secondary pages like
- Contact info
- privacy policy
- Blog
- Support
Create an HTML Sitemap
Think of it as a guide that helps users find what they’re looking for. It can help with crawlability and navigation. Place it at the end of the page and keep it updated regularly.
Handle Pagination Properly
In place of endless scroll, use numbered pagination (Page 1, 2, 3...)
This gives search engines a clear path through long lists of content or products. Also, include rel="next" and rel="prev" tags where they are needed.
Fix or Customize Error Pages (404s, etc.)
Never let your visitors exit when a page doesn’t exist. A custom 404 page with links back to important areas like home, blog, and services improves user experience and keeps people from going back.
Boost Site Performance
Site performance is not just about convenience. It is based on a ranking factor. A slow site call pulls down your SEO best practices, affects user experience, and decreases conversion rate. Even a 1-second delay in load time can cut down conversion by 7%.
Here is how to make your website lightning fast.
Measure and Improve Your Site Speed
Start by benchmarking your current page.
Use tools like
Your main focus should be on metrics like
- First Contentful Paint
- Largest Contentful Paint
- Time to Interactive
Find where the issues are and solve them one by one. Most speed problems are fixable and worth fixing.
Use a CDN and Browser Caching
A content delivery network keeps copies of your website on global servers. It delivers content from the closest server to the user, which speeds things up.
Browser caching tells your visitors’s browsers to remember common site elements so they don’t need to reload them every time. This decreases time for repeat visits.
Use services like
- Cloudflare
- BunnyCDN
- AWS CloudFront
Set caching rules for images, stylesheets, scripts, and fonts.
Compress Large Images and Assets
Images are usually the biggest files on a site. That means they’re the biggest drag on speed.
- Resize before uploading (don’t scale huge images with CSS)
- Use proper formats like WebP or AVIF
- Compress with tools like TinyPNG or Squoosh
Also compress CSS and JS files using tools like
- Gulp + UglifyJS
- Autoptimize (for WordPress)
Every kilobyte counts!
Avoid Excessive JS That Blocks Rendering
JavaScript, if placed heavily or very poorly, can delay how fast your page becomes usable. Both users and your site performance take a hit.
To fix it:
- Lower inline JS and scripts in the
- Use asynchronous loading
- Remove the script you don’t need
Optimise Server Response Time
Even on a clean website, everything can break if the server is slow. Run a test either on WebPageTest or GTmetrix and check Time to First Byte. It should be under 200ms.
If not:
- Move to faster hosting
- Use object caching
- Optimise database queries
- Check for tools or scripts slowing the backend
Server performance sets the ceiling for your site speed.
Check Server Location
Distance will add delay if your traffic is in India but the server is in the US. Go for a hosting provider with data centres where your primary audience is. Or else depend on a CDN to close the gap.
Bonus tip: Test with the KeyCDN to see how fast your site loads around the world.
Limit Excessive External Links
Every time your page pulls a script or font from another domain, it creates a connection delay. These can slow things down.
- Don’t use third party fonts, tools, and embeds
- Use self host fonts and scripts when possible
- Limit ad scripts and affiliate links
Only include what truly adds value.
Avoid Duplicated Pages From Architecture Issues
Duplicate pages generally create confusion for search engines and waste crawl budget.
Find:
- URLs with and without trailing slashes
- HTTP vs HTTPS versions
- www vs non-www
- Filtered or paginated pages create duplicate content
Fix them with:
- Proper canonical tags
- 301 redirects
- Consolidated URLs in internal links and sitemaps
Keep things clean. One page is equal to one purpose.
Optimise for Mobile Users
These days, mobile devices make up over 60% of all web traffic. If your site doesn’t work well on phones, you are turning away the majority of your audience, and this will affect your SEO best practices.
Make Sure It Has a Responsive Design
Your website should adjust smoothly across all screen sizes. It should be usable on every device.
- Test site pages on mobiles, tablets, and both small and large screens.
- Use Chrome DevTools to preview different devices.
- Content should never require horizontal scrolling or pinch zooming.
If it does, your layout needs work.
Test Popups on Mobile
Google and users dislike intrusive popups on mobile. If you're using popups for email capture, discounts, or alerts:
- Make sure they’re easy to dismiss.
- Don’t cover the whole screen.
- Use slide-ins or top bars instead of modal popups.
Also test how they appear on smaller screens. What looks clean on desktop might be a disaster on mobile.
Optimise Mobile Page Size and Image Loading
Mobile users often browse on slower connections. To improve experience:
- Keep the page size under 2 MB.
- Use lazy loading for images.
Test page weight with GTmetrix or PageSpeed Insights The faster, the better.
Check Mobile Usability in Search Console
Google Search Console provides real feedback from users. Go to the Mobile Usability Report and look for issues like:
- Text too small to read.
- Clickable elements too close together.
- Content wider than screen.
If there is a problem, fix it on the spot. This is direct insight from Google about how your website performs on mobile devices.
AMP Setup and Validation
AMP setup and validation are still appreciated. But,
- The role of AMP has shifted since its initial peak in popularity. Google no longer requires AMP to appear in Top Stories on mobile.
- AMP is still a helpful option for fast-loading mobile pages.
- Validation ensures AMP pages are indexed and displayed correctly.
- Not essential for all sites, but still important for performance-focused platforms.
Use the AMP Test tool to check each page.
Make Button or Tap Targets Easy to Use
Small buttons or tightly packed links are difficult to use on touchscreens.
Follow this rule:
- Buttons should be at least 48x48 pixels
- Leave space between clickable elements
- Avoid hover-only elements (mobile users can’t hover)
Test your forms, CTAs, and menus on real phones, not just emulators.
Mobile Favicon and Navigation Experience
It might seem minor when a favicon is missing but it affects how your site looks in browser tabs and search results on mobile.
Also:
- Keep mobile navigation minimal and easy to tap
- Use a hamburger menu or bottom nav bar
- Don’t overload the menu with too many items
The goal is clarity. Make it obvious where to go next, even with one thumb.
Nail Your Page With Core SEO Elements
Maybe your page is fast and looks great, but if the core elements are messy, unclear, or even missing, you are not going to convert or rank well. These on-page basics matter a lot.
Proper Use of Heading Tags (H1, H2, H3..)
Headings are the core part of how Google understands your page. They are not just for styling.
- Only one H1 is needed per page
- Use H2 for major sections
- Use H3s and H4s for subpoints or subheadings
For better SEO content optimization, avoid skipping levels, as it helps both users and search engines to understand and read your content better.
Unique and Optimised Page Title
The title tag is shown in the search result. It is one of the strongest on-page SEO hint. Keep these things in mind:
- Put your main keyword close to the front
- Make each title unique across the site
- Keep it under 60 characters
A good title = better click-through + better rankings.
Write a Clear, Compelling Meta Description
While they don’t affect rankings, they do help attract clicks, which means more visitors.
A great meta description:
- Gives page clarity
- Speaks to the user’s intent
- Include primary keyword
- Stays under 160 character
If you don’t write a meta title, Google will randomly pull text that will not look good.
Don’t Use Meta Keyword
Still using < meta name ="keywords" > ?
Stop.
It is very old, and Google ignores it. In fact, it can even trigger spam signals. Delete it from your code. Simple always works best.
Instead, incorporate schema markup so that AI chatbots can optimize their understanding and functionality.
Also provide more detailed answers and take actions for your clients.
Fact: AI chatbots can better interpret information, which leads to more precise responses and smoother customer interactions.
Clear Call To Action (CTA)
Every page needs a next step, so what should a visitor do?
- Start My SEO Growth
- Claim My Free Audit
- Get Ranked Now
- Unlock Organic Traffic
- Let’s Optimize My Site
Add a convincing (and not pushy) and visible CTA above the fold and repeat it lower on the page for skimmers.
Accessible and Easy to Use Forms
People will bounce if your form is gawky and confusing.
Fix it by:
- Clean labeling fields
- Keeping the numbers in field minimal
- Using validation and error messages that are easy to understand
- Making sure form work on mobile and keyboard
Accessibility is important for users and compliance.
Use Favicon, Cookie Notices, and Privacy Elements
Always remember the legal and visual basics.
- A proper favicon helps brand recognition in browner tabs
- Cookie notices are now required under GDPR and similar laws
- Privacy policy and terms pages should be linked in your footer
You just need to cover what is important. It shows users and search engines that your site is reliable and complete.
Deep Keyword Research & Audit
Keywords still matter a lot. But it’s not about overstuffing them with content or chasing volume without vision. A strong keyword audit helps you line up your content with real search intent.
Let’s walk through the essentials.
Do Complete Keyword Research
Start with real data and do not just guess. There are some tools that help to:
- Find primary and secondary keywords
- Discover long tail keywords and questions people may ask
- Analyse keyword intent and difficulty
Don’t focus on high volume terms. Find keywords with clear intent that match what your site offers.
Map Keywords to Appropriate Pages
Every page needs direction and a keyword it’s built around.
- Map one primary keyword per page
- Add a few supporting keywords that naturally fit
- Don’t target the same keyword on multiple pages (we’ll get to that in a sec)
Create a simple spreadsheet that connects each URL with its target keyword set. It makes your strategy easier to manage.
Different types of keywords for a website
1. Informational Keywords
These are used when someone is searching to learn, understand, or explore a topic. The purpose here is to gain knowledge, not purchase, yet.
Example: “how AI improve SEO”
(The user is looking for insights or recommendations and is not ready to buy.)
2. Commercial Keywords
These show that the user is considering a purchase and comparing options. They are in the research phase and evaluating what is best.
Example: “Best AI tools for Content Marketing”
(The user is narrowing down choices and planning to buy soon.)
3. Transactional Keywords
These are used when the user is ready to take action, like buying, booking, or signing up. The purpose is immediate and clear.
Example: “Buy SEO Audit Tool”
(The user knows what they want and is ready to complete the transaction.)
4. Navigational Keywords
These are used by users, like brand names, website names, or specific product names, to locate specific websites or webpages, indicating their intended destination.
Example: “Ahrefs” or “SEMrush”
(The users generally know about the product and want to reach a certain website or webpage.)
Add Keywords in Titles, H1s, H2s, and Content
Since you got the keywords you are targeting, put them where they make sense:
- Page title
- Meta description
- H1
- H2s and subheadings
- First 100 words of your content
- Image alt text (if it fits naturally)
Do not overstuff keywords anywhere in the content. Write humans first content and then add keywords smartly where they make sense.
Avoid Overuse of Keywords
Targeting the same keyword across multiple pages?
That is keyword cannibalisation and it confuses search engines. You end up competing with yourself only. To make things right:
- Combine similar pages into one strong page
- Downgrade the weak page and let the stronger one lead
- Use internal linking to strengthen the right URL
Also, watch out for overuse of any keywords. If you repeat the same phrase more than twice, it makes content feel like it is generated by a robot.
Benchmark Branded and Non-Branded Search Performance
Always make sure to check how you are doing on:
- Branded terms like your company name, product names
- Non-branded terms like anything your audience searches without knowing you
Using some tools like Google Search Console and Ahrefs can show:
- Which keywords are driving traffic
- Where you're underperforming
- Which terms need more content or optimisation?
Tracking both helps you understand brand awareness vs search reach.
Align Homepage With Primary Brand Terms
Your homepage should rank for your brand, no question.
Make sure it includes:
- Your full brand name should be in the title, H1, and content
- A clear description of what you do
- Internal links that reinforce brand context
If your homepage isn’t ranking for your own name, something is off.
Competitor Analysis For Content and Backlinks
If you are willing to rank, you need to know what you are against. Understanding your customer is important. It is how you find out what is working, what is missing, and where your biggest opportunities are hiding.
Let’s break it down.
Identify Top Competitors
Google your most important or primary keyword. Find out who your real competition is in the top results. Study them. Don’t focus on the brands you think are your competition. Focus on the ones who are actually ranking.
There are tools like Semrush and Ahrefs that show you a domain level competitor based on keywords.
Tip: Don’t just copy big players like Amazon or Wikipedia. Look for real competitors with similarly sized sites, products, or services.
Analyse the Top Keywords
After you have picked your competitors, it is time to see what is bringing them traffic.
Use a keyword tool to check:
- What keywords they rank for
- Which ones bring in the most traffic
- Where they outrank you
Over 90% of pages get no search traffic, and the main reason is weak or missing keyword focus.
Look for:
- Keywords you are not targeting at all
- Pages where they rank higher than you
- Opportunities for long-tail keywords or low difficulty wins
Benchmark Their Traffic, Content Strategy, and Backlinks
Once the competitors list is there, now the goal is to figure out what they are doing differently. Check their:
- Calculate monthly organic traffic (using Semrush or SimilarWeb)
- Top performing content types (guides, product pages, blogs)
- Backlink count and referring domains
- Content update frequency
- Site structure and UX
Find the answer to the following:
- Are they publishing more often than you?
- Do their posts get shared or linked more?
- Are they using more visuals, videos, or tools?
This is your benchmark.
Find Content and Keyword Gaps
Growth can be as simple as finding what your competitor missed and delivering it.
Run a content gap analysis, which will show:
- Keywords they rank for, but you don’t
- Topics they cover that you have missed
- Pages they have built links to that you have not created yet
Look for keyword messes and themes and not just individual terms. This will help you build complete topic coverage. It is something Google now heavily rewards. Semrush and Ahrefs make it easy to find missing gaps in content and keywords.
A strong internal content cluster can boost rankings by up to 40% when it fills previously uncovered topics.
Use Insights to Enhance Your Own Strategy
Never copy what is already ranking. Take data of what is working and build something better. This is what is called the ‘skyscraper SEO technique.’ Find the best content out there, then make yours taller, sharper, and more useful.
Follow these steps to do that:
- Write better content on the same topic (make it more helpful, easier to read, and straight to the point)
- Go after targeted words your competitors missed (particularly those with low competition and high intent ones sitting in the gaps.)
- Create visual assets your competitors don’t have (tables, charts, comparison graphics, even simple tools.)
- Pitch to the same backlink sources but with more valuable pages (make it a better page with more depth or fresher info.)
If they are ranking with a 1,000 word article or blog, write a 1,500 word piece with better formatting, internal links, and unique insights. If they have ignored the video, add a short walkthrough. If they are ranking with thin content, go deeper.
Optimise Images Across the Site
Images can help your SEO or they can completely drag down your site if you are not careful. If the pages are slow loading, have missing alt text, or have giant uncompressed files, it can kill both your rankings and user experience. Let’s fix that.
Compress All Images
Having big sized images on the website is one of the top reasons websites load slowly. Every kilobyte matters and on mobile too. You can use tools like TinyPNG, ImageOptim, or ShortPixel to compress files without hampering quality.
- Keep JPEGs under 100 KB
- Use WebP where possible
- Avoid BMPs and TIFFs entirely
Use Descriptive ALT Text
ALT text isn’t just about accessibility. It tells Google what your image shows and how it fits into the page.
- Bad:
alt="image1" - Better:
alt="modern office chair with mesh backrest" - Best:
alt="Ergonomic mesh office chair under 5000 for home office"
This boosts image rankings and makes your site easier to use for people with screen readers.
Fact: Over 74% of sites don’t use alt text for their images and that’s a big miss.
Remove Dead Images
Broken image links look unprofessional, waste page space, and make your site load slower. Audit your site and:
- Fix any 404 image links
- Remove old images that are loading
- Update or replace missing visuals
Tools like Screaming Frog or Ahrefs Site Audit can help find dead image URLs fast.
Avoid Large Images (>100KB Where Possible)
If your page has 10 images over 100KB, that’s an extra 1MB+ of weight. Multiply that across dozens of pages and you’ve got a problem. Compress, resize, or replace bulky files. Use vector icons or SVGs where possible.
A report from HTTP Archive says that images account for 50%–60% of a typical web page’s total weight.
Don’t Rely Too Heavily on Stock Images
Google wants unique content, and that includes visuals. If your site is stuffed with generic stock photos, it’s going to feel stale.
- Use original product photos, illustrations, charts, or custom screenshots
- Crop or edit stock photos to avoid the “template look”
A study by NNGroup found users ignore stock photos that don’t match the content or seem “too polished.”
Enable Lazy Loading If Needed
Lazy loading means your images only load when they’re about to be seen. This cuts down your initial page load time and makes the site feel faster.
On WordPress? Just enable lazy loading in your theme or with plugins like
- WP Rocket
- a3 Lazy Load
- Smush
If you’re building a custom site, add loading="lazy" to your
loading="lazy" to your
Google recommends lazy loading for large, image-heavy pages to improve mobile performance.
Content Quality & Optimisation
Google content is not about filling keywords. It is about helping people. It is about helping people. And if your site is full of low-effort, outdated, or broken content, Google notices. So do users.
Let’s clean that up.
If a page can’t explain itself in more than a couple of sentences, it probably doesn’t need to exist. Google sees pages with fewer than 200 words as “thin” and may ignore or even penalise them.
This does not mean that every page needs to be long. But if it is a core URL, like a service, category, or blog, it needs to be substantial, helpful, and on point.
According to Google’s Search Quality Evaluator Guidelines, pages should offer unique description, depth, and purpose to be considered high quality.
Create Timeless and Regularly Updated Content
Old content ages fast. Topics like “Trends in 2021” or “Top tools this year” won’t help your site in 2025.
Make sure:
- Core guidelines and blog posts are updated yearly (or more)
- Your product/service pages reflect current offerings
- Stat, tools and links are valid
Evergreen content like tutorials, how-to’s, or detailed guides keeps pulling traffic long after it’s published.
Fact: Just updating your older blogs could give you a 100%+ traffic boost.
Fix Grammar, Spelling and Readability
Errors kill credibility. If your writing feels scrambled or is full of typing errors, people won’t trust what you are and may not come back. Use tools like Grammarly, Hemingway, or just a human proofreader.
Read it out loud. If it doesn't sound clear and natural, rewrite it.
Keep sentences short and clear. Break up paragraphs. Make your content feel like a conversation, not a wall of text.
Avoid Duplicate or Copied Content
Don’t copy and paste from anywhere.
When the same content shows up in more than one place, Google may not rank it as high. Focus more on original writing, insights, and adding value beyond what is already out there.
Use tools like Copyscape or Siteliner to find duplicate content issues and fix them.
- Each product page should have a unique description
- Don't spin or reuse other blog content without rewriting it
Use Mixed Content Like Images, Texts, Videos
Add visuals to explain your point faster and break the repetition. People don’t usually like to read long paragraphs.
Here is what works the best:
- Images to show steps or data
- Short explainer videos or even animations
- Charts or infographics to present stats
- Clickable elements like tabs
Over 80% of consumers have been persuaded to buy after watching a brand’s video.
Make Sure Fonts and Contrast are Easy to Read
Design plays a big role in readability. People will never stay long on your page if your font is too small, too light, or hard to read.
- Stick to clean fonts for web content
- Keep the contrast strong so your text is easy to see
Pro tip: Use Google’s Lighthouse or WebAIM Contrast Checker to test accessibility and fix these issues.
Keep Hyperlinks Clear and Working
Broken links are equal to bad experiences.
- Check for 404s and redirect chains using Screaming Frog or Ahrefs
- Make sure buttons or anchor text don’t lead to dead ends
- Use descriptive anchor text like “Download SEO Checklist” instead of “Click here.”
Internal linking also helps Google crawl your site and users find more helpful pages.
Make the Contact Page Easy to Find
Don’t let your visitors search too much on your page to find contact info. Your contact page should:
- Be easy to access from the main menu and even the footer of the page
- Add a working form, phone number, and email (if needed)
- Be easy to use on mobiles
- Load fast and clearly explain how/when you will respond
Have a Strong Privacy Policy and TOS
Even if users don’t read the page policy, Google does. A visible Privacy Policy and Terms of Service page shows you are a transparent and trusted page.
- Link them in your footer
- Make sure they are current and easy to understand
- Add GDPR or CCPA info if you collect user data
Improve User Experience (UX), including Website QA testing
Great SEO starts with great UX.
It doesn’t matter how many keywords you rank for. If a user doesn’t want to be on your site, they will bounce. And Google pays attention to that.
Let’s fix the UX issues that most websites miss.
Make Sure Your Have A Clean Homepage Design
Think of your homepage as your site’s main entrance. Users won’t stick around if it is cluttered, confusing, or slow.
Keep it clean:
- Limit distraction and excessive use of animations
- Put your core value in the front
- Prioritise clarity over creativity
Test Usability Across Important Internal Pages
Don’t just test your homepage. Most people will land on product, service, or blog pages directly from search.
These pages need to:
- Be easy to use on all devices
- Launch fast
- Have clear headings or visuals
- Have clear CTAs
- Work properly on every browsers
Pro tip: Use tools like Hotjar or Microsoft Clarity to watch how people interact with your content and fix anything that makes them hesitate.
Use Videos and Visuals Wisely
Adding videos is great. But it needs to load fast and make sense. Don’t use heavy, uncompressed background videos. Focus on:
- Explainer videos on service pages
- Short how-tos in blogs
- Embedded YouTube (if bandwidth is a concern)
Fact: 91% of consumers want to see more online video content from brands.
Make Sure Navigation is Clear
A confusing menu structure destroys the whole UX. Here is what you can do:
- Keep the nav bar simple
- Limit downdrop levels
- Highlight the important pages first
- Add navigation aid (breadcrumbs)
Avoid Aggressive Popups or Too Many Ads
Popups can work but they also ruin experiences.
Don’t show the popup the second someone lands on your page; just wait for 10 seconds.
Also:
- Don’t layer multiple popus at once
- Make ot easy to close them
- Avoid full screen popups, as it can ruin rankings
Too many ads? That is another UX killer. Users don’t trust sites that look like ad farms.
Make CTAs Clear and Relevant
If users can’t figure out what to do next, they will bounce.
Your calls to action (CTAs) should:
- Be visible without scrolling too far
- Match the page intent (e.g. “Get Pricing” on a pricing page)
- Use simple, specific language like “Start Free Trial” or “Schedule a Call.”
Pro tip: Keep testing CTA placement and wording using A/B tools like Google Optimise or VWO.
Do Regular Website QA Testing
Best designed website can also break in the background. That is where QA testing comes in. You need to make sure everything works exactly how it should when there is any big updates or design changes.
Here is what to check:
- Broken links or missing images
- Forms that don’t submit or throw errors
- Buttons that go nowhere or overlap on mobile
- Layout shifts on different screen sizes
- Issues on different browsers (Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge)
Run through your site on mobile, desktop, and tablet. There are free tools to use like BrowserStack or test manually. Test across all key pages like the homepage, product, blog, checkout, login, and everything.
Bonus tip: Ask someone who’s never used your site before to test it. Fresh eyes catch stuff you’ve been ignoring.
QA isn’t a one-time thing. Make it part of your monthly checklist. Catching issues early is way easier (and cheaper) than losing traffic because your site stopped working right.
Study Your Backlinks & Authority (Backlink Strategy)
Strong backlinks can make a big difference in how well you rank on Google. But it is not about the quantity of the links generated. Google cares about link quality, relevance, and natural patterns of the content.
So if you want to rank higher, you need to take backlink study very seriously and make a backlink strategy.
Let’s break down how you can make a backlink strategy.
Total Backlinks and Referring Domains
Start with finding answers to some of the basic questions, like how many websites are linking to you? Or how many unique websites are doing it?
You can use tools like
Look for trends:
- Are your backlinks growing over time?
- Are you getting links from new domains or the same few ones?
Also, focus more on referring domains than raw backlink count. Ten backlinks from ten different sites are better than fifty from one.
Look for Unwanted Links and Disvow Them
Bad links can affect the SEO if they look manipulative or irrelevant.
Check for:
- Links from low-quality listing sites
- Foreign language pages with no importance
- Sites with virus or adult content
- Over optimized anchor text
Suggestion: If you spot fake links, reject them through Google’s Disavow Tool.
Use Proper Anchor Text Planning
The anchor text used when someone links to you helps search engines understand your page.
Here is how you can keep it sounding natural:
- Use some general or even exact match terms
- Use targeted words only where they make sense
Keep an Eye on Lost or Broken Backlinks
Sometimes pages go offline, sites restructure, or people remove your links. This is how great links disappear.
Use tools to:
- Find lost backlinks
- Reach out and request a replacement
- Redirect dead pages that were previously linked
Also check for broken links indicating to your site. You don’t want to waste that link equity.
Audit Competitor Backlinks
See who is linking to your competition. Look up 2 or 3 direct competitors and export their backlink data. Then:
- Find backlinks from blogs, media sites, or listing websites in your niche
- Look for broken links
- Use their guest post and PR strategies
This is one of the easiest ways to find relevant and real backlink opportunities.
Avoid Link Exchanges or Suspicious Backlink Practices
Google now detects unnatural link building more easily than before.
Avoid:
- Buying links from Fiverr or shady sellers
- Comment spamming on forums or blogs
- Private Blog Networks
You might see a temporary boost, but if Google catches it, the damage can last a long time.
Review International Search Engine Optimisation
If your business targets users in more than one country or language, then doing international search engine optimisation is important.
International search engine optimisation helps you rank better in different countries and languages.
Let’s walk through the important factor.
Use hreflang for Multi language or Multi Region Content
If your site has pages in more than one language or different regions, you need hreflang tags. Hreflang tells Google:
- This page is in French and is for Canada
- That one is in Spanish and is for Spain
- Another is in English and is for the UK
This helps avoid duplicate content issues and ensures the right page shows up in the right country. To manage language and regional versions, Google recommends hreflang in XML sitemaps for bigger websites.
Translate Site Content Properly
Don’t be dependent on Google Translate or any other translation tools. Bad translation affects the conversion rate. If you are targeting users in another country, invest in professional translation (human, not AI) to capture local hints.
It’s not just about swapping words. It is more about making content culturally relevant.
Fact: More than 70% of people prefer browsing sites that are written in a language they understand.
Structure International URLs Correctly
There are three common ways to set up international URLs:
- ccTLDs
- Strong signal to Google for country targeting
- Requires separate SEO efforts for each domain
- Subdirectories
- Easier to manage
- Shares domain authority
- Subdomains
- OK if treated carefully
- Slightly weaker signal than ccTLD
Google generally prefers subdirectories for search engine optimisation efficiency, unless you already have ccTLDs for business reasons.
Set Target Countries in Search Console
It helps you guide Google by setting a target country for your content.
If you are using a gTLD (like .com) and targeting India, the UK, or the US, go into GSC and set that location.
Steps:
- Go to Settings → International Targeting
- Choose the country you want that section of the site to target
This helps Google understand your intentions, especially if you’re not using country-code domains.
Note: You don’t need this for ccTLDs like .fr or .in. Those are already geo-targeted.
Build Localized Backlinks and Optimize for Local SERPs
Backlinks still matter but international optimisation calls for local links.
If you are trying to rank your Spanish version of a page, you should get links from Spanish websites. Not just any website.
Here is what to focus on:
- Partner with local blogs and publications
- Submit to country-specific sites
- Build local citations (especially for service-based businesses)
- Sponsor or collaborate with regional influencers
Optimise for local SERPs
- Use local language and currency
- Include address or country-specific details
- Add location-specific keywords naturally into titles, headings, and meta descriptions
Watch for Negative SEO Practices
Sometimes the thing you are missing is what affects the search engine optimisation. It is what you are doing wrong. This red flag can tank your ranking fast. Here is what to double-check and clean up.
Remove Hidden Texts or Cloaked Content
Google hates deception. If your site uses hidden text like white on white or text pushed off-screen with CSS, that is a big red flag for Google. The same goes for cloaking. Showing one thing to the user and another to Google. It can slip by unnoticed, but it’s a real issue.
Check for:
- CSS display:none on keyword-stuffed blocks
- JS that hides text on load
- Serving different content based on user-agent
Pro Tip: Use tools like Google’s URL Inspection Tool to see exactly what Googlebot sees.
Avoid Doorway Pages and Meta Refreshes
Doorways are basically thin pages that are designed to rank on specific keywords and then redirect users elsewhere. They might seem clever, but Google can come down on them hard.
Meta refreshes can also launch spam signals.
If you need to redirect, always use 301 or 302 server-side redirects, not sketchy tricks.
Google says their goal is to show people content that’s useful and matches what they’re looking for.
Prevent JavaScripts Redirects and Iframes Abuse
JavaScript redirects can be legit but when abused, they look shady.
For example, if you're using JS to redirect users instantly after a page loads, that’s suspicious. The same with iframes that hide harmful or irrelevant content under the hood.
Avoid:
- JavaScript that automatically redirects users to affiliate offers
- Iframes that display untrustworthy third-party pages
- Redirects only visible to search engines
Don’t Overdo Popups, Ads or Affiliate Links
If you want to monetise, that is fine. But when the ads start overwhelming, Google takes notice. In fact, Google’s “Page Layout Algorithm” targets pages where the top half is mostly ads, especially on mobile.
Official Source
And what if your site is filled with affiliate links and little original content? That’s thin content plus over optimisation, which equals trouble.
What to watch for:
- Too many ads above the fold
- Fullscreen popups blocking the content
- Affiliate heavy pages with little real value
If you’re using affiliate links, add rel="sponsored" to avoid penalties.
Make Sure Your Site Is Not Blacklisted or Sandboxed
Websites with malicious code, misleading content, or spam tactics can get blacklisted by Google. This could happen without your knowledge if your site was hacked.
Also, if your site is new or has a thin backlink profile, it might be stuck in Google’s sandbox. It is a kind of probation period where your pages are indexed but not ranking well yet. It is not an official penalty, just a temporary filter that holds back newer or less trusted sites.
Check your status:
- Run your domain through Google’s Transparency Report
- Use security tools like Sucuri SiteCheck or VirusTotal
- If blacklisted, follow Google's Security Issues Report in Search Console and clean up immediately.
- If you suspect sandboxing, focus on building high-quality backlinks and improving overall trust signals on your site
Getting out of both situations takes action but it is totally doable if you stay on top of it.
Conclusion
Website optimisation isn’t something you do once and forget. It is an ongoing and repetitive process. User expectations are always changing, and search engines are always changing how they rank websites. This implies that you should monitor the performance of your website on a regular basis rather than just once a year.
Keep tracking your SEO metrics. Fix what is slowing you down. Improve what is working. And most importantly, use real data to guide every update you make.
If this all feels like a lot, don’t worry, you don’t have to tackle it by yourself. MSM Coretech helps businesses like yours simplify and smoothen the entire optimisation process, from fixing technical issues to improving content and UX, so your website actually delivers the results you built it for.
Related Blogs
Top 10 SEO Strategies to Boost Website Traffic in 2026
Boost your website’s visibility in 2026 with these 10 proven SEO strategies. Discover how to increase organic traffic, improve search rankings, enhance user experience, and build a sustainable online presence in an ever-evolving digital landscape
Read More

Voice Search & Accessibility: Preparing Websites for 2026 Search Landscape
Voice search and accessibility will shape the 2026 search landscape. This guide explains how businesses can optimize websites for natural-language queries, AI-driven search behavior, and inclusive digital experiences that meet global accessibility standards.
Read More

Can AI Improve Your SEO Strategy? A Complete 2026 Guide
See how AI upgrades your 2026 SEO strategy. Discover smart tools, practical tactics, and data-driven methods to boost rankings and traffic.
Read More



