Dominance of React Single Page Application

Single Page Applications, also known as SPAs, are a kind of web app that process, stack up, and update content dynamically. The components are updated without refreshing the full page.
Being very different from traditional websites, single page applications use advanced tools and technologies to improve user experience by eliminating interventions and offering a seamless interface. This helps a web user to communicate with applications smoothly.
The most significant advantage is the eradication of full-page reloads, thus rendering the web experience more responsive and fascinating. This is attained by making sure that all the essential technologies, from HTML and react to CSS codes, are working fine. This means on a single trigger or request, the context should be updated as per the user’s action.
When a user clicks on any action in a single-page application, it should only reflect the required information to your browser and the browser should act accordingly. Developers are increasingly using single-page applications (SPAs), and they have a variety of options when it comes to selecting the appropriate frameworks and libraries.
In this blog we will provide you with an understanding of SPA Frameworks, its strengths and weaknesses and why one should consider developing a Single-page application using React.
Top 5 Single-Page Application Frameworks And Libraries
React
React, usually known as React, is an open-source JavaScript framework. It was created by Meta (formerly known as facebook) in 2013. The main use of this technology is to develop a React Single Page application. React is also used alongside other libraries and frameworks, such as Redux to oversee states, React Router for easy navigation, and Axios to deal with API requests. React is very famous among developers because of the performance, simplicity, and efficiency it offers.
| Highlighted Features |
|
| Restrictions |
|
Angular
Angular is the other framework listed and was introduced in 2010 by Google as AngularJS. It introduced two-way data binding and dependency injection, two features that revolutionized web development, and it is an open-source web application framework. It is used for developing critical enterprise-level applications. This technology helps businesses to develop web applications that provide smoother user experiences and outstanding performance.
| Highlighted Features |
|
| Restrictions |
|
Vue.js
Vue.js, also commonly known as Vue, was founded in 2014 by Evan You (a former individual who worked on AngularJS at Google) and got famous for its clarity and flexible integration. It is a JavaScript framework used to set up UI. The tool is described as a progressive framework because it follows an instrumental adoption approach. This means it lets developers use its capabilities in small steps, which makes it flexible enough to work on projects of all sizes and levels of difficulty.
| Highlighted Features |
|
| Restrictions |
|
Next.js
Next.js is an open-source framework and was founded in 2016 by Vercel. It is a framework that builds on the capabilities of React, which means it offers features like SSR, SSG and in built API routes. This makes it a top choice for developing well-performing single-page applications. It has the capability to improve SEO without any heavy configuration. It is widely popular among developers or enterprises wanting to build scalable and production-ready SPAs with better user and search experiences.
| Highlighted Features |
|
| Restrictions |
|
Nuxt.js
Nuxt.js was first released in 2016 and is an open-source framework based on Vue.js. It is designed to help developers create the finest single-page applications, server-side rendered apps, and static sites with minimal configuration. Nuxt adds a strong structure to Vue development by offering convention-over-configuration, automatic routing, and powerful rendering modes. It is a top choice for developers who want the flexibility of Vue combined with performance optimizations and SEO benefits for their SPAs.
| Highlighted Features |
|
| Restrictions |
|
SPA Technologies: Strengths & Use Cases
|
Technology |
Strengths |
Use Cases |
| React | Component-based, virtual DOM, rich ecosystem (Redux, React, Router) | Dashboard, e-commerce, social platforms |
| Angular | Full-featured framework, TypeScript-based, built-in routing and testing |
Enterprise apps, admin panels |
| Vue.JS | Lightweight, flexible, easy to integrate, grate for gradual adoption |
Progressive web apps, startups |
| svelte | Compiles to optimized JS, minimal runtime, fast rendering | Lightweight SPAs, performance-focused UI |
| Next.js | React-based with SSR and SSG support, great for SEO | Hybrid SPAs needing SEO |
| Nuxt.js | Vue-based with SSR, modular architecture | SEO-friendly Vue SPAs |
Significance of React Single Page Application
React can be used to develop everything, including native apps, single-page web apps, and very complicated enterprise applications. But it is becoming very popular because it can make single-page applications and works better. Over 98% of websites on the internet today are built using Reactjs which is more than 49 million.
The library is built on a strong base and is growing smoothly as a collection of libraries, tools, and frameworks like Redux, React Router, Material UI, Grommet, Ant design, and others. Additionally, the code written in React works well with the markup that client-side libraries render on the server.
Here are some of the top reasons behind why one should develop a Single-page application using React.
Peak Performance: React doesn't change the DOM directly when users interact with it. In place of that, it uses a virtual version of the DOM. This lets developers test all the changes related to the virtual DOM first, so they can figure out how risky the changes are ahead of time.
This means that only the changes that need to be made are shown on the web page when you do things on the virtual DOM. This makes the app run faster and ensures that users have an outstanding experience.
Code Stability: The technology only allows data flow in one direction while utilizing downward data binding just to make sure any changes on the child app do not affect the parent application. This means if the developer makes changes to any object, it will be compulsory for them to alter its state with a proper revision. This provides the code a better stability.
React Components: It is a component-based framework that lets developers divide its user interface into many small and reusable components. This makes the app development and testing prices simple. The a change made in one part of the web app won’t affect the other components due to that. The JSX framework allows developers to code with loosely coupled components. These components receive HTML and make rendering simpler for other subcomponents. To sum it up, React allows developers to code custom components and build complex ones for high-volume applications.
An active community of developers: The technology has active community support because the environment has a wide range of tools for generating user interface animation, code testing, and much more. The popularity and community involvement of React has more than 180,000 stars and 1,500 regular contributors on GitHub. Meta is also making efforts to develop, deploy, and enhance the library based on feedback before they release a new feature. Tech experts are always posting tutorials and answering developers' questions on social and professional sites like YouTube, Stack Overflow, and Quora. That means you will never be stuck in the problem.
Easy testing: The web apps developed on React are very easy to test, increasing the development process and delivery of applications. This is exactly why companies looking to release their web app swiftly in the market use React. It also delivers quick release with better quality.
Best UI development: For an application to be a success, the UI plays the most significant role. User interface is the first look through which users judge you and consume your service or start a communication with your brand. A bad interface can affect your business in a negative way. The React framework allows you to build interactive user interfaces using its declarative components.
Developer's tool: Having the best technology is good but it will not be very effective if it cannot offer tools to analyze and test its own deployments. For instance, Meta understands that it is a major requirement and it devised React developer tools and Chrome dev tools. There are some major developer tools that assist them to find the child or parent components. These tools also allow developers to view component hierarchies and inspect the component’s state and props.
Real-World Use Cases of React Single Page Applications
The wide adoption of React Single Page Applications in industries is due to their ability to provide a cordial, app-like experience of browsing with swift speed in navigation and dynamic updates of the content. The nature of loading their content automatically without loading the whole site makes them suitable for such platforms, which require speed, responsiveness, and high user interactions.
1. SaaS Dashboards and Analytical Tools
Current SaaS products are supported by real-time data display and interactive charts as well as smooth UI transitions. React SPAs are commonly used to display data live so that the use of CRM tools, analytics dashboards, HRMS portals, and financial reporting systems does not disrupt user flow. The component-based design allows easy control of multifaceted views and often changing UI overhauls.
2. E-Commerce Websites and Marketplaces
React SPAs suit well those online stores that allow visitors to navigate the assortment of goods, place goods in carts, and use filters over and over again. The SPA architecture minimizes the delays of loading, increases the speed of product discovery, and makes checkout faster. These advantages assist in reducing the bounce rates and increasing the conversions, particularly to sites that contain high inventories.
3. Social Media and Community Platforms
Each of the applications, which require constant interactions, such as posts, messages, likes, comments, and notifications, should have instant updates to the UI. Such a common dynamic will occur on the frequency of change, which is why React is a useful tool to address this type of change, and that is the reason why SPA architecture is the preferred general preference of many social applications, discussion communities, and collaboration tools.
4. Online Learning and Streaming Platforms
SPA Uninterrupted content transitions in ed-tech platforms, video streaming sites, and virtual classrooms are made possible in React. Users often change lessons, play videos, or try to do quizzes, and SPAs make sure all is loaded without any reload disconnects.
5. Booking, Travel and Ticketing Systems
Applications that contain searches with recurrent queries, filters, seat selections, and checkout processes are extremely useful regarding SPA performance. React makes these workflows responsive and easy to use, making users happier. React SPAs can eventually be the final choice in any application that needs to be fast, interactive, and provide an uninterrupted experience in terms of browsing, which is the reason they can be the favored option in scalable digital products.
Steps to Develop a React Single Page Application
There are multiple steps involved in creating a React single page application, starting from configuring the development environment to deploying the finished product. Let's discuss the whole procedure:
Step 1: Set Up Your Development Environment
To start with your React app, you must have these on your system:
- Any Integrated Development Environment (IDE) that supports React.
- The latest version of Node.js: It is a JavaScript runtime domain, which is very important to control your project and is essential for managing your project reliances.
Tip: To use it, install it from the official website of Node.js. - The latest version of React App: It is a tool that sets up a new React project with a standard structure and configuration. To install it, run the following command in your terminal:
npx create-react-app my-react-spa
When you run this terminal, it will:
-
- Use npx (Node Package eXecute) to fetch the latest create-React-app package without installing it globally.
- Create a folder named my-React-spa.
- Set up all the default React boilerplate files inside it.
- Install the necessary dependencies automatically.
Once the things mentioned above are done, you can go inside the folder and start the app:
cd my-React-spa
npm start
Note: If you are using Node 18 or later, Create React App still works, but the React team now recommends using Vite or Next.js for new projects because CRA is a bit heavy and slow to build.
IDE that supports React: Use an integrated development environment, or any code editor like VS Code, to write and manage your code in an efficient manner.
Step 2: Structure Your React Project
Once you open the created project folder, you will see something like this:
my-React-spa/
├── node_modules/ (All installed dependencies - auto-generated)
├── public/ (Static files like index.html, favicon, images)
│ ├── favicon.ico
│ ├── index.html
│ └── manifest.json
├── src/ (Main source code for your React app)
│ ├── App.css (Styling for App component)
│ ├── App.js (Main App component)
│ ├── App.test.js (Tests for App component)
│ ├── index.css (Global styles)
│ ├── index.js (Entry point of the application)
│ ├── logo.svg (React logo)
│ └── report WebVitals.js (Performance measuring)
├── .gitignore (Files/folders Git should ignore)
├── package.json (Project configuration & dependencies)
├── README.md (Basic project instructions)
└── yarn.lock / package-lock.json
Step 3: Organise Your Files
The default structure works fine for small projects. But as your app increases, it is important to create folders inside src/ for better separation. Example of a common setup:
src/
├── components/ (Reusable UI components like buttons, headers, cards)
├── pages/ (Page-level components like Home, About, Contact)
├── assets/ (Images, fonts, icons
├── styles/ (Global styles or CSS modules)
├── utils/ (Helper functions)
├── App.js
├── index.js
Step 4: Create Components
A React single page application is built using small components. The components are small and reusable pieces of user interface (UI). These components are easier to build, manage, and handle. Here is how you can create components:
Example: Let’s create a simple ‘Header’ component.
src/components/Header.js
import React from 'React';
function Header() {
return (
< h1>Welcome to My React SPA
);
}
export default Header;
Now, use it inside your main application component:
src/App.js
import React from 'React';
import Header from './components/Header';
function App() {
return (
This is a simple React single-page application.
);
}
export default App;
After this, when you run ‘npm start,’ you will be able to see your ‘Header’ at the top, followed by the text paragraph.
Step 5: Add Routing
One of the main features of a React single-page application is the ability to move between different views or “pages” without reloading the entire browser. In React, we achieve this using React Router, a popular library for routing.
Install React Router: In the project folder, open a terminal and run:
npm install React-router-dom
Create the Pages:
Create two new components, ‘Home.js’ and ‘About.js,’ inside the ‘src/components’ folder.
Create the Pages: Create two new components, ‘Home.js’ and ‘About.js,’ inside the ‘src/components’ folder.
src/components/Home.js
import react from 'react';
function Home() {
return (
Home Page
Welcome to the home page of your react single-page application.
);
}
export default Home;
About.js
src/components/About.js
import react from 'react';
function About() {
return (
About Page
This is the about page where you can describe your app.
);
}
export default About;
Update the App Component:
Set up routing in src/App.js using react Router v6 syntax:
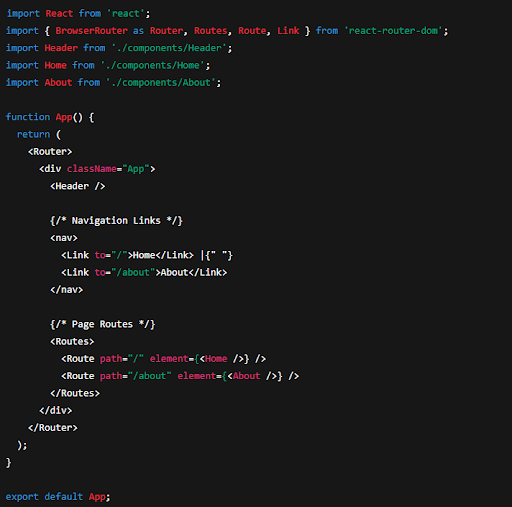
Step 6: Style Your Application
Styling is an integral part of a development process because it makes your application visually appealing and easy to use. When developing a Single-page application using react, you can style components using Plain CSS (most common for beginners), Sass (for advanced nesting and variables), and CSS-in-JS libraries like styled-components. For now let’s use plain CSS
Create a CSS file: In your project, you already have src/App.css. Open it and add:
src/App.css
.App {
text-align: center;
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
}
header {
background-color: #282c34;
padding: 20px;
color: white;
}
nav {
margin: 20px 0;
}
nav a {
color: #61dafb;
margin: 0 10px;
text-decoration: none;
}
nav a:hover {
text-decoration: underline;
}
Import the CSS in App.js:
Make sure App.js has: import './App.css';
Run Your App:
Start your app: npm start
Once this is done, your header will have a dark background, your navigation links will be styled, and the text will look clean.
Step 7: Fetch Data from an API
Web apps generally pull data from a particular server. In react SPA, you can use the built-in Fetch API or a library like Axios for cleaner syntax and extra features.
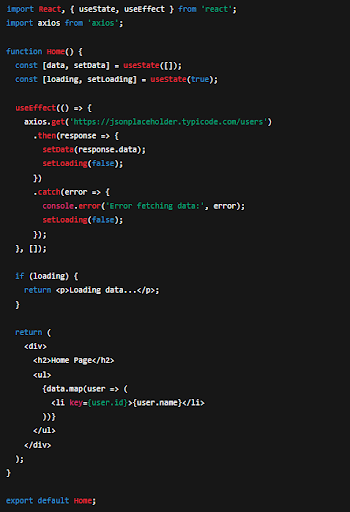
Step 8: Deploy Your React SPA
The application is now ready and you can make it live so others can use it. Use popular free hosting options include Vercel (fast and easy), Netlify (also great for beginners), and GitHub Pages (perfect for personal projects and portfolios). Here is how you can deploy on GitHub Pages.
Add the homepage field
In your package.json, add:
"homepage": "https://username.github.io/my-React-spa"
Note: Replace ‘username’ with your GitHub username and ‘my-React-spa’ with your repo name.
Install gh-pages
npm install gh-pages
Add deployment scripts
Inside package.json under "scripts," add: "predeploy": "npm run build", "deploy": "gh-pages -d build"
Deploy
Run: npm run deploy
This will build your project and push it to the gh-pages branch of your repository. Your app will be live at the URL you set in the "homepage" field.
Optimise the Performance of Your React SPAs
- Lazy Loading: Execute code-splitting tools and techniques like dynamic import or React lazy loading to make sure the page is loading only the required components of the code. This minimizes the bundle size and improves the loading time.
- Memoization: Utilize memoization approaches like shouldComponentUpdate for class components or React.memo for functional components to avoid needless re-renders and boost efficiency.
- Systematic Data Fetching: Reduce the quantity of data sent between the client and the server by optimizing data fetching through the use of strategies like pagination, endless scrolling, or on-demand data loading.
- Server-Side Rendering: Use SSR to improve the initial load time and take care of search engine optimization issues, either by putting in place a custom SSR setup or by using a solution like Next.js.
- Performance Observance: Observing the performance of your React single page application using tools like React DevTools, Lighthouse, or any React performance based libraries like React-pref-devtool.
- Code Improvement: Inspect and improve the code regularly, remove unwanted complexity, decrease bundle sizes and for optimal performance, use techniques like memorization or code splitting
- Image & Asset Optimization: Use strategies like content delivery networks (CDNs), image compression, and lazy loading to maximize the delivery of images, fonts, and other static assets.
- Progressive Web App Approach: Take into consideration putting in place a Progressive Web App (PWA) approach, which can boost the overall speed of your React-based SPA, decrease the initial load time, and improve the offline experience.
Artificial Intelligence In SPA Development
If you use AI coding tools along with your SPA framework, you can build things faster and with less manual work.
AI coding tools are used to automate, enhance, and smoothen the single-page application development process. They minimize the boring coding work and make design changes automatically. It delivers an outstanding user experience without any manual work.
Few possibilities on how AI can help in the SPA development process:
- Code generation tools (NLP) to understand the queries and generate code fragments live, which minimizes coding duration and helps developers focus on difficult problems.
- AI Tools to automate the whole process of testing and debugging faster and more precisely than humans.
- AI-powered tools helps in design automation by suggesting and adjusting layout. This optimizes images and delivers outstanding web design, which is easy to use.
- AI tool for content creation that creates text, videos, or even images from a simple prompt. This makes content generation faster and effortless.
- UX enhancement by analyzing data to generate website content and interactions based on each user's needs.
- AI-powered SEO recommendation tools that help get insights and automate website optimization and boost visibility.
Putting together SPA frameworks with tools like GitHub Copilot, Codestral, or Qodo can boost their creation through intelligent code suggestions, auto-refactoring, and component generation. These tools help by acting like a smart coding assistant while you build your single-page application.
Here is how these AI tools can help you:
- Use Intelligent code suggestions as they predict what you are about to type and suggest complete lines or functions. It ultimately brings off some time and efforts.
- Auto-refactoring tools can rearrange or improve code for better performance and readability without changing the way it works.
- Use Component generation tool, because a simple description in plain English (a simple prompt) helps generate a component, and the tool can generate the initial code for it, which you can then change.
- Error-spotting tools to catch potential bugs or missing imports before you even run the app.
- Offers Learning aid which means it shows you patterns and best practices while you code, which is handy if you are still learning React or SPA structure.
Conclusion
React is a strong and popular JavaScript library for developing smooth and interactive Single page applications (SPAs). It helps developers to instantly develop difficult and responsive web applications with component-based design and the virtual DOM of React. It is very important to carefully measure the advantages and limitations of using React SPAs for your upcoming project. Having knowledge of all the limitations, like slower initial loading times and search engine optimization problems, helps smoothen the development process.
If you are looking for an expert team to assist you professionally, MSM Coretech is here to offer top-grade React development services to help your business fulfill the needs and requirements. Invest today in our quality React development and get the most scalable, sustainable, and productive application that can grow with your business.
Related Blogs

Website Development Cost in USA
Explore website development cost in USA for 2026. Learn pricing by website type, features, phases, and factors that impact total cost.
Read More

Benefits of Outsourcing Web Development Projects in 2026
Explore the benefits of outsourcing web development projects in 2026. Learn costs, models, and how to choose the right web development outsourcing company.
Read More

Top 10 Websites Based on Python
Explore top websites based on Python, like Netflix, Uber & Reddit and learn why a website development company uses Python for scalable, secure web apps.
Read More



