Everything about single Page Applications (SPAs)

There are some popular apps like Gmail, Facebook, Twitter, and Trello that work this way. You will also notice how quick and smooth it feels when moving around. This is because most of the data is there, and only the required part will be changed and reflected on the screen. These applications use JavaScript structures (React, Angular, or Vue) to make all this happen in the backend. These techs help developers build more engaging as well as faster websites. These websites feel modern and easy to use. SPAs are built to make the web experience feel more like a smooth application, fast and easy to use.
Develop blazing-fast, unprejudiced, user-first web apps that dominate the digital experience. Single Page Applications have reshaped the very essence of interacting with modern-day websites. The moment an individual clicks a link, it is a new webpage that loads in the traditional set-up. Unlike traditional setups, SPAs operate inside a single HTML file, updating content on the fly with JavaScript. This essentially allows for a smooth and snappy navigation experience that comes close to that of a mobile or desktop application.
With the users expecting hill-sprint-fast execution and real-time response, SPAs have never been more relevant. They deliver high-performing web applications capable of keeping their users engaged and content. This is the age of business owners and developers realizing how SPAs have narrowed the user experience gap between native apps and websites.
What is Single-Page Application (SPA)?
A single-page application is basically described as a web app or a site that feels fast and smooth to use. These websites give users a touch of mobile application. These websites load everything once at the start and then only update what is needed as you go, in place of loading a brand new page every time a user clicks on something. A user can stay on the single screen the entire time.
How Single Page Application Works
When a user opens a page on the website, it loads the basic framework of the site. The layout, menu, and design will be the same all the time. But when a user clicks on something, for example, opening a product, checking their profile, or even switching the modules, the website will just pull the data and show that exact content in no time, without reloading the whole page from the start.
This concludes-
- User don’t have to wait for the entire page to reload
- The user gets smooth changes like flipping between screens in an app
- A user gets good experience on poor connections
Key Characteristics of Single Page Applications
1. Dynamic Content Loading:
With AJAX and APIs, SPA can load and show new content very quickly. SPAs uses AJAX to create loading of web pages faster, which makes the surfing experience with smoother transitions when surfing to new pages.
2. Client-Side Rendering:
The user’s browser is where most of the action takes place. All the necessary HTML, CSS, and JavaScript are loaded the first time. The app then “interacts” with itself again through JavaScript and changes the view by working with the DOM.
3. Decoupled Back-end:
In most SPAs, the front-end and back-end are clearly separated. The frontend of an SPA usually uses an API as the backend. This makes the backend flexible and lets the code be used on different platforms.
4. Rich User Interfaces:
SPAs can change parts of the page that aren’t connected to the main topic and only change those parts when the system tells them to, without having to restart the whole page. This makes it possible for SPAs to offer a slightly better and more dynamic experience, like native apps.
5. State Management:
SPAs usually use some kind of advanced state management technique to understand and keep track of the data and UI state of the app. This helps to ensure that views and interactions are always consistent.
Single Page Application vs Traditional
- SPA (Single Page Application): Loads one HTML page. Navigation happens without any page refresh. The system fetches and renders data dynamically.
- MPA (Multi-Page Application): With every page, a new HTML document gets loaded. Better for content-heavy websites.
- JAMstack (JavaScript, APIs, and Markup): The front end is separated from the back end, which builds fast and secure websites, offering content via CDN.
Read: JAMstack SSG
Working of SPAs
The "Single Page Application" workings are mostly centered around client-side rendering (CSR). Therefore, upon landing on a single-page application, the user only loads the initial HTML, CSS, and a bundle of JavaScript. After this, all the data and content updates happen asynchronously in the background, possibly through Fetch API/Axios/GraphQL. In the next step, the user then interacts with the page in the way that JavaScript executes changes to applicable sections of the DOM without refreshing the page.
The SPA request lifecycle
- The browser requests the initial document.
- The server returns a bare-bones HTML file and sends the bundled JavaScript and CSS files.
- JavaScript starts the application and then loads the initial interface.
- Interaction with a user causes JavaScript to get further data from the APIs.
- JavaScript only modifies the related elements of the UI, which prevents a complete page reload.
Key Concepts Behind SPAs
- Virtual DOM: Allows faster UI updates by listening to changes in a virtual representation of the DOM.
- Hydration: Merges minimal HTML served by the backend with JavaScript-powered features.
- Routing: The client-side routers (such as React Router and Vue Router) manage navigation and URL changes like an MPA, except without reloads.
Key Benefits of Single-Page Applications
For a lot of good reasons, SPAs have become very popular among mobile application development company in Jaipur. You and the creator can both find SPAs useful because they make things easy.
Come with us as we go over these benefits:
Smooth User Experience: Users undergo seamless transitions between pages. Interactions feel instantaneous because delays due to server responses or full page reloads never occur. SPAs use JavaScript to swap views, update components, and provide instant feedback.
Lower Bandwidth and Server Load: Once the server is loaded, the SPA now will not request an HTML page from the server. It will rather ask for data. The bandwidth usage drops to a large extent, and the server no longer feels the load at that level. As more action and any logic happen on the customer side, the server starts getting raw data through APIs.
Mobile-Friendly Behavior: SPAs mimic the behavior of native apps. Hence, they favor a mobile-first implementation, such as quick transitions, offline caching with service workers, and push notifications.
Greater Stability: Along with caching and lessened data use, these features make it possible for the pages to be shown even when internet connections aren’t working properly.
Better UX: Users are more interested in and have a better experience with the material when pages load faster and look like they can be interacted with.
Faster Development: Multiple APIs can be used with SPAs, which lets developers work on the frontend, backend, and links that drive content in a more smooth way.
Easier Debugging: Codebases are often more flexible, which means that developers can code on different parts at the same time. This also applies to testing and bug fixes.
Cross-platform Compatibility: SPAs can be made to run on any platform or browser because they only need one set of code. This means that users can have a smooth experience even when they switch devices
What Are The Popular Examples of Single Page Application?
Single-page applications have become the support system of many popular platforms that require speed, interactivity, and responsiveness. Here are some of the popular examples that show how SPAs redefine user experience in 2025:
1. Gmail -
Gmail has a UI that allows the fluid environment of communication wherein users may read, compose, and navigate between separate mails without ever triggering a page reload. Content updates with responsiveness and offline abilities make this app highly functional when a user's bandwidth is constrained.
2. Trello -
Trello is an interactive drag-and-drop task management board supported with real-time updates. Users collaborate, drag cards, and update boards at lightning-fast speed without halting for server reboots or refreshes.
3. Notion -
Notion provides navigation and live updates within the application, which gives users a smooth interface like a desktop inside their browser. It is one of the most flexible platforms if a user wants to do project management, take notes, and create collaborative workspaces.
4. Figma -
Figma is a website-based design and prototyping tool that provides a detailed space where one can edit in real time collaboratively. Although browser-based, it behaves with the speed that a true native app should behave.
5. Google Maps -
Google Maps manages way too much data but has a smooth and responsive UI, all happening from the client side. Panning and zooming are undeterred by mentions of real-time directions.
Why Businesses Are Opting Single Page Applications?
The digital world now has more expectations than ever before when it comes to speed, performance, usability, and digital experience. SPAs are a great way to address these objectives.
Let’s look at some of the most important things that have made SPAs a good choice for a website development company.
1. Better User Experience
User experience is the most important thing for SPAs. Page reloads are necessary for multi-page apps. This breaks the flow of the user and makes it harder for them to reach their objective. SPAs provide consumers a smooth experience like a desktop or mobile app, so they don’t have to refresh pages.
2. Performance
Performance is always important for online apps, and SPAs may be faster after the first load, which is a big plus. SPAs may make page or data interactions happen faster by loading the main app code on the initial load and the data it needs on the run.
3. Mobile-First Style
People are quickly moving away from using the internet on their computers and toward using it on their phones. They want web apps that work like native apps. SPAs are great for mobile devices because they feature flexible interfaces and use data efficiently. They offer users the quick reaction and engagement they expect from using mobile app development services. Also they don’t require a separate native app to do the same things.
4. Real-Time Features
Many new on-demand apps require real-time capabilities such as live chat updates, and collaborative editing. SPAs are simpler to work with when it comes to real-time functionality because of how they are built. The SPA can get and show changes without having to refresh the whole site since it stays connected to the server.
5. Offline Capabilities
In a world that is becoming more mobile-friendly, it’s hard to be able to grow offline or with a weak connection. SPAs feature a client-side architecture that lets them work offline. After the user loads the first app, they can do a lot of things even when they don’t have a connection. When they do have a connection again, the data will sync.
Challenges & Limitations of SPAs
There are several good things with single-page apps, but there are also some typical problems with them, such as:
- Difficulty Scaling: SPAs frequently rely on a small number of servers to load and maintain the user experience. This might lead to more traffic or problems with presenting the website.
- Security Risks: Because much of the hard work is done on the client’s side, SPAs are nevertheless vulnerable to attacks that might add harmful code that runs in the browser. Following the right security steps, such as using a Content Security Policy (CSP), may stop these attacks.
- SEO Disadvantages: Since an SPA only shows one page at a time, it is still hard to optimize them for search engines that reward depending on the number of pages and the amount of information created. However, Google has started to provide SPAs greater tools for indexing.
- Site Analytics: As just one page is being generated, it will be hard to figure out how many people are visiting the site or where they leave the customer journey.
- Navigation Challenges: To avoid having to scroll awkwardly on a website, content must be tailored to suit the current user experience with each new display of information. These worries also apply to navigation since the back button doesn’t work the same way in an SPA.
- JavaScript: If a user has JavaScript turned off, due to any reason, SPAs won’t operate. JavaScript is needed to create the user interface that an SPA depends on, which might be an issue in certain cases.
- Memory Leaks: Some frameworks might allocate RAM even when it’s not required, which can slow down the application.
SPA vs MPA vs SSR vs SSG
Choosing the architecture will perfectly fit into the goals of the project. Consider:
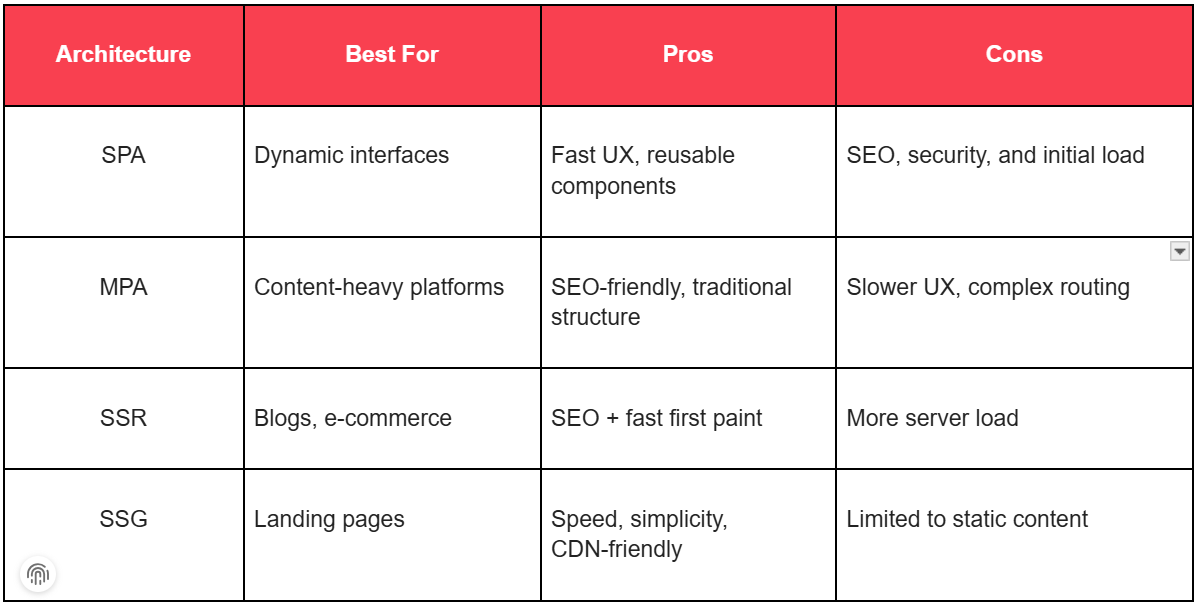
A decision tree or matrix can be used to determine exactly how an application fits its needs.
How to Create SPA (Single Page Application)?
1. Environment Setup: You can start by structuring your application using Vite, Create React App, or Angular CLI.
2. Reusable Components: You can design your user interface components so that they can be used smaller and bigger. Design with atomic principles in mind.
3. Routing & Navigation: Make use of either React Router or Vue Router and also make use of nested and dynamic routes.
4. API Integration & State Management: You use Fetch or Axios or service-side GraphQL endpoints while helping the client-side services communicate with the back end. State management could occur in Redux, in Zustand, in Pinia, or in Vuex.
5. Deployment: Any kind of deployment is quickly handled by Vercel, Netlify, or Firebase. Test and publish the builds on the go through CI/CD pipelines.
Advanced Concepts
- SSR with SPAs allows SPAs to serve fully processed HTML pages to bots or users, thus improving SEO or time-to-first-byte (TTFB).
- SSG for hybrid applications combines with interactive SPA with static process to allow faster loading and SEO.
- Micro frontends are basically big applications that are divided into smaller applications using different teams to make the maintenance easier.
- WebAssembly integration is used for important and critical situations like video processing, 3-D, or AI.
- AI personalization allows customized content and UI depending on user preferences or behavior analysis.
Search Engine Optimisation for SPAs
Use these modern techniques, including
- Prerendering, which means improving web loading during the building time for search engines.
- Dynamic rendering, which processes in a different way depending on the user agent.
- Edge rendering, which means processing the HTML on the edge within the CDN before delivery.
- Structured data is the use of JSON-LD schema to clearly define your content for search engines.
- Headless CMS integration means your content is stored in separate systems (for instance, Strapi or Sanity) and is queried via APIs.
Implementation of Performance Optimization
The techniques here are worth using:
- Lazy Loading: Loading the very exact components and assets.
- Code Splitting: Division of code into pieces, with the help of different tools (Webpack, Rollup, or Vite).
- Tree Shaking: Kills the code that is sort of dead halfway.
- Caching Strategies: Apply cache-up sites for offline use for the consumer to fetch data using React Queries.
- Performance monitoring: Tools for performance analytics (Lighthouse, Core Web Vitals, New Relic, and Sentry)
SPA Security Best Practices
These practices are important for secure SPAs:
- Use HTTPS to mitigate any kind of man-in-the-range attacks.
- Use JWT and OAuth2 as they handle secure authentication.
- Use input validation to cleanse all input information.
- Use CSRF and XSS protection; it works with tokens on the server side and escape outputs on the client side.
- Give role-based access to the users, as they must never be able to access areas they are not authorized to.
Future of Single Page Applications (SPAs)
- Edge computing brings processing closer to users by cutting down the response time.
- UI/UX designs by AI offer on-point interfaces that adjust to behavioral patterns.
- Innovations like resumability (eliminates rehydration bottlenecks), streaming HTML (enables faster perceived load times) and partial hydration (activates JavaScript only where interactivity is needed) are emerging.
The Best Frameworks For Your SPA
Adversaries may start to pick a method for their SPA now that they know more about how single-page apps work. Depending on the specific demands of an organization, these frameworks, which are structures for designing programs and interfaces that interact together, may be employed to get the most out of an SPA. Below are some of the most common frameworks for making Single-Page Applications:
- Angular: Angular is one of the best frameworks out there. Google runs it, and it has alternatives for client-side technologies. It is quite responsive, with fast loading times and simple navigation. Angular is also fantastic for apps that provide and receive information, including news, weather, travel, and social media apps.
- React: This framework was created by Facebook and has a list of UI components that may make it easier to build real-time apps. Dashboards, online storefronts, and job portals are some examples of dynamic content that work well with it. ReactJS is also better for SEO since Google can read it.
- Vue.js: The VueJS framework is straightforward to use and has drag-and-drop tools that make it easy for developers to get started with the components they need most. This makes it great for newcomers. It is also rather easy for developers to utilize CSS with it.
- Aurelia: This open-source framework is licensed under MIT and interacts with other frameworks to make development more versatile. Aurelia is a newer player in the sector that makes setting up configurations easier and supports a variety of languages, such as TypeScript.
- Backbone.js: Backbone is better for smaller pages, but it doesn't support data binding, which might slow down bigger apps. However, it usually works quickly with smaller data sets than more widely used frameworks like Angular.
Read : React Single Page Application
Conclusion
Fast yet interactive and scalable solutions offered by SPAs are a true need today. With the right set of tools and proper architectural considerations, they can be made Google-friendly, secure, and efficient.
Key Points:
- SPAs mend the UX gap between web and native apps.
- Performance, SEO, and security must be integrated into the planning phases.
- Framework and architecture choices should directly reflect project goals.
When you aspire to create a product that feels smooth, loads swiftly, and engrosses users, SPA architecture is your best friend.
FAQs
When should a business choose a Single Page Application over a traditional multi-page architecture?
A business would use a single-page application when interaction with the user, real-time and application-like performance are paramount. SPAs are also optimally appropriate in dashboards, SaaS services, collaboration services, and data-driven products in which continuous optimization and clear navigation have immediate effects on productivity and retention.
How do Single Page Applications impact scalability and long-term maintenance for enterprises?
The SPAs are useful in maintaining scalable architecture with decoupled front-ends and back-ends. This isolation enables independent scaling, reuse of API across platforms easily, and can be developed in parallel by more than one team, and this is much more maintainable and not costly compared to any long-term technical debt of enterprise applications.
Are Single Page Applications secure enough for business-critical applications?
Yes, properly invested. Enterprise-grade SPAs are HTTPS-based, have support for secure authentication software such as JWT or OAuth2, rigid input validation, and very strict safeguards against XSS and CSRF attacks. Through adequate security structure and control, SPAs have the potential to achieve high standards of compliance and data protection.
How do SPAs affect SEO and analytics for B2B websites and platforms?
Server-side rendering, static site generation, prerendering, and structured data can be used to optimise modern SPAs to be search engine-friendly. In case of analytics, event-based monitoring and virtual page tracking tools guarantee proper insights into the user journey, so in case of SPAs, lead-generation and content-based B2B platforms are also feasible.
What business outcomes can organizations expect after adopting a Single Page Application?
Improved user experience, less server load, and low engagement rates are common indicators of improved performance in organisations. In the case of B2B products, it results in improved customer satisfaction, more complex features adopted, a shorter development process, and a more competitive advantage in digitally-driven markets.
Related Blogs

How Much Does Website Development Cost in Jaipur?
Learn the website development cost in Jaipur, including pricing by type, features, platform, SEO, and maintenance. Plan your budget and choose wisely.
Read More

How to Develop Content Generating Website like ChatGPT?
Complete 2026 guide on development costs, features, tech stack, and implementation. Start your AI Website project today.
Read More

Top Web Development Trends 2026 | Latest Web Technologies
Explore top web development trends 2026, latest web technologies, AI, cloud, DevOps, IoT, and future-ready solutions for businesses.
Read More



